コンプリート! greenhouse gases effect diagram 307323
Browse 355 greenhouse effect diagram stock photos and images available, or search for sun to find more great stock photos and pictures Greenhouse Effect On Earth, Greenhouse Gases Absorb Infrared Radiation Emitted From Earth And Reradiate It Back, Thus Contributing To Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides
Understanding The Greenhouse Effect Learn Biology
Greenhouse gases effect diagram
Greenhouse gases effect diagram- Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, andForm definitions of the greenhouse effect based on prior knowledge, class discussion, and viewing diagrams 2 Participate in group brainstorming sessions and class discussions related to the impact of the greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Analyze global warming diagrams and resources to obtain a clear understanding of this scientific




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric CO 2 This happens because the coal or oil By increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, we're amplifying the planet's natural greenhouse effect and turning up the dial on global warming GuideThe diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphere
Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight But unlike those gases, greenhouse gases are not transparent to outgoing heat (longwave infrared radiation), which radiates from the sunwarmed surface of Earth day and nightGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician Joseph Five Major Greenhouse Gases The most significant gases that cause global warming via the greenhouse effect are the following Carbon Dioxide Accounting for about 76 percent of global humancaused
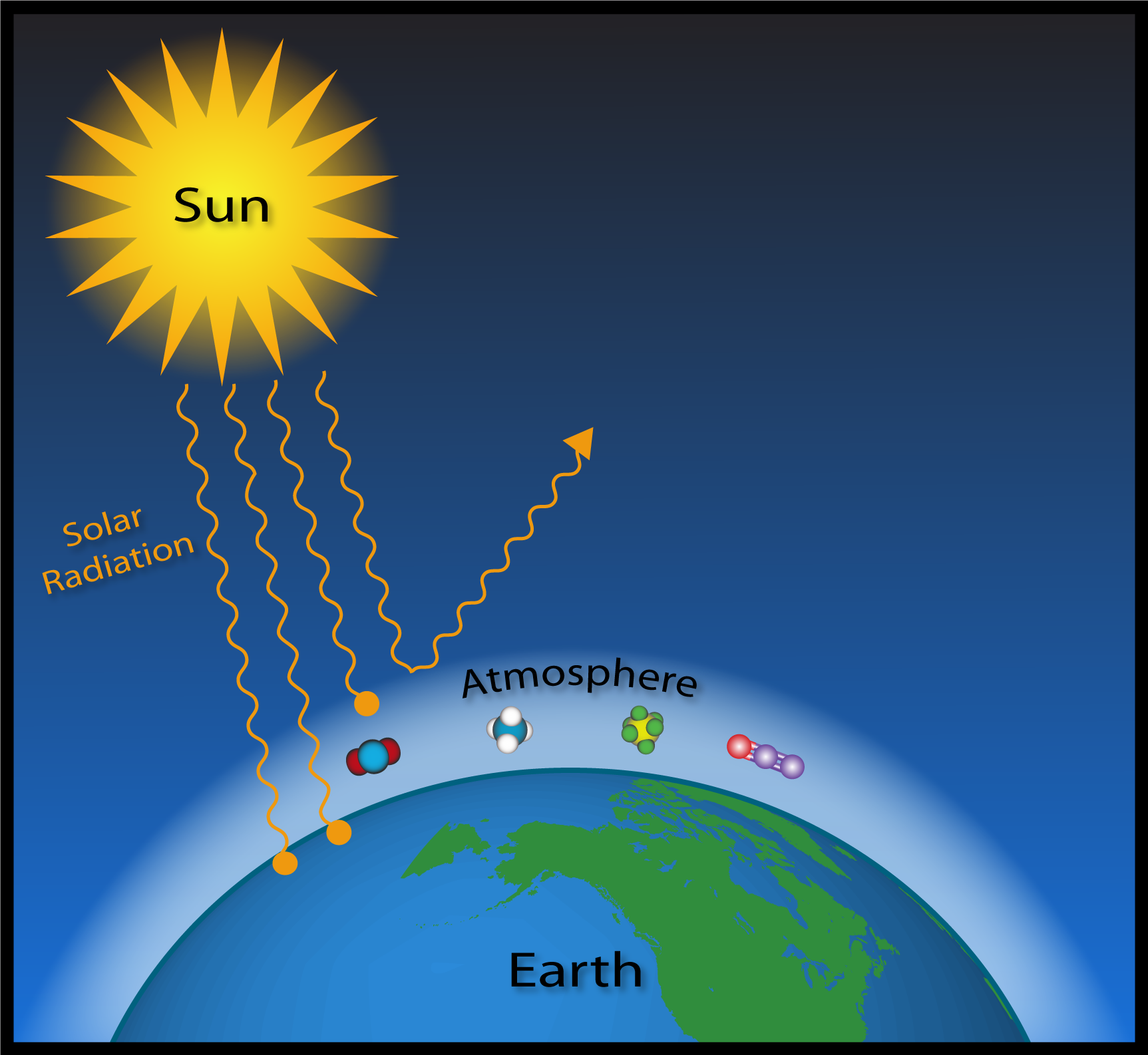
Analyze their greenhouse gas emissions Then they will participate in a greenhouse experimental demonstration and finally demonstrate their knowledge of the greenhouse effect using a puzzle (Appendix A Diagram) Prior Knowledge & Skills • Introductory knowledge of the greenhouse effect • Data gathering skillsGreenhouse Effect Shown above is an Infrared Map of the Earth Red areas represent regions of high heat retention in the atmosphere This is an equatorial band because that is where the atmosphere has the most water vapor The earth has a natural greenhouse effect due to trace amounts of H 2 0 and CO 2 that naturally occurThis diagram explains to us about the greenhouse effect Basically what greenhouse effect is, is the sun, which emits mostly long radiation and shortwave radiation, all this radiation comes in in the morning or during daytime without any problem The atmosphere, which has various kinds of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, little bit of carbon dioxide, et cetera, these radiations basically pass through



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate
That approach in effect makes carbon dioxide, CO 2, the prevailing "currency" of greenhouse gases and global warming Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC)Global Warming The Greenhouse Effect Model Storyboard That is a great way for students to combine images and text in a creative way to produce quick and clear scientific diagrams Students are going to recreate a model of the greenhouse effect using arrows to show how radiation movesThis diagram explains to us about the greenhouse effect Basically what greenhouse effect is, is the sun, which emits mostly long radiation and shortwave radiation, all this radiation comes in in the morning or during daytime without any problem The atmosphere, which has various kinds of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, little bit of carbon




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons



Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some ofThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence ofGreenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factors




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download
Greenhouse gases are not a bad thing in themselves, but too much of them in the atmosphere leads to an increase in the greenhouse effect and global warming This article tries to answer a question about the greenhouse effect "Greenhouse gases prevent the infrared rays from leaving the Earth's atmosphere, but why do they not prevent additional solar radiation from entering the atmosphere?" The key is the different wavelength (or different frequency) of solar light and infrared light Let's have a look at the greenhouse effect The major natural greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 3670% of the greenhouse effect on Earth (not including clouds);




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Graphic Vector Illustration Stock Vector Illustration Of Pollution Planet
Human Activity and the Greenhouse Effect What greenhouse gases do humans generate? Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount ofGWP values are calculated as a ratio of the combined effect of these factors if 1 kg of the gas in question is injected into the atmosphere compared to the effect if 1 kg of kilogram of CO 2 is injected CO 2 is assigned a value of unity, so the resulting ratio is the GWP GWPs for a few selected gases are given in the table




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing How The Greenhouse Effect Works Global Warming Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Global Warming Steemit
Carbon dioxide CO 2, which causes 926%; Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does notCarbon dioxide (CO 2), which causes 9–26 percent;




Illustration Of The Greenhouse Effect Due To Greenhouse Gases Mainly Download Scientific Diagram




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphereThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng
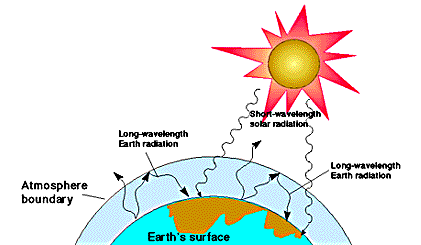
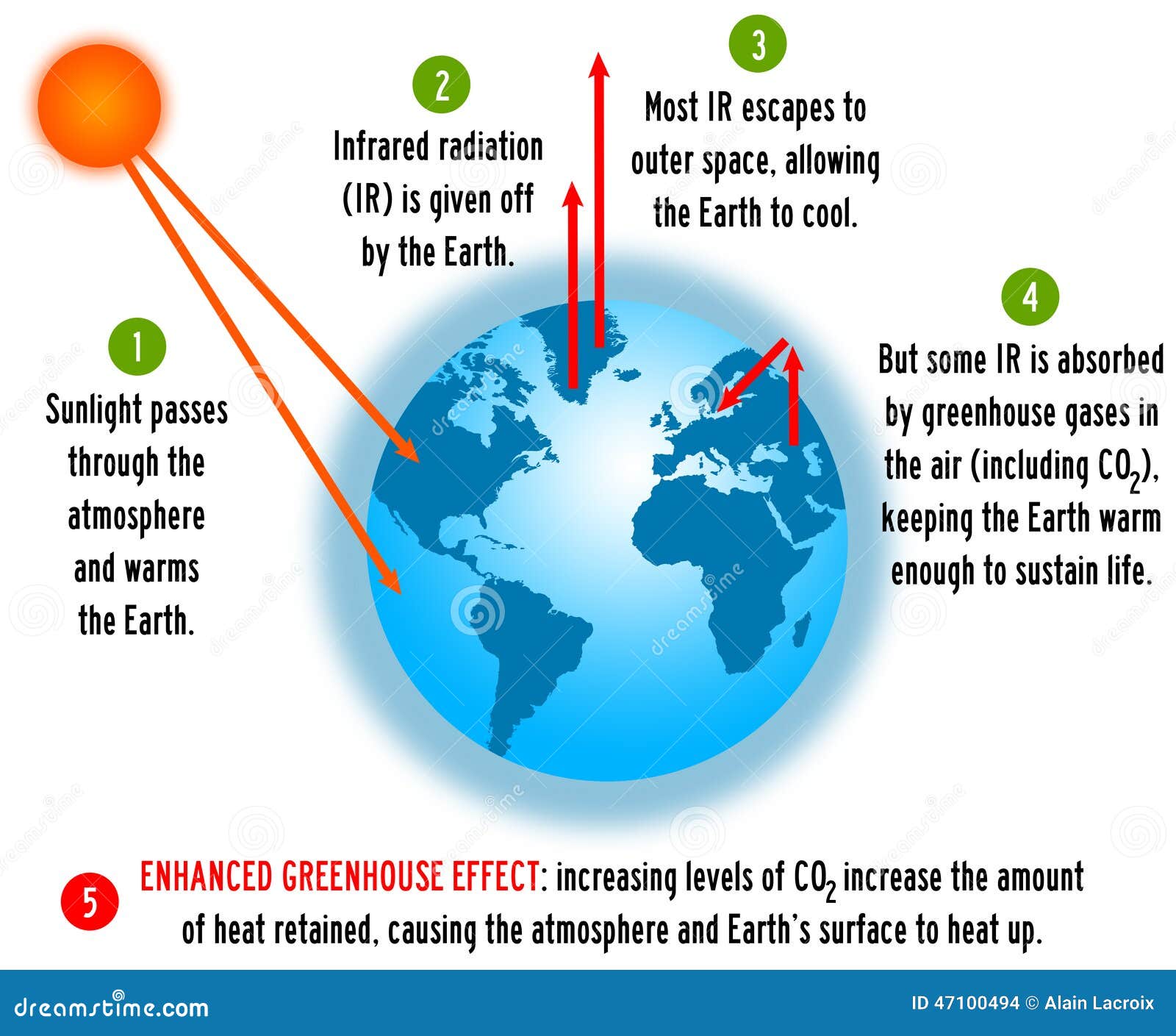
The effect of increased greenhouse gas concentrations The natural greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into spaceThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, theDuring a volcanic eruption, the main greenhouse gas that is emitted is carbon dioxide During an eruption, huge amounts of CO₂may be released (approximately 026 Gt/y globally), leading to an overall heating of the earth and its atmosphere through an accelerated greenhouse effect, often referred to as global warmingFor example, in 1991, Mount Pinotubo released over 05 Gt of
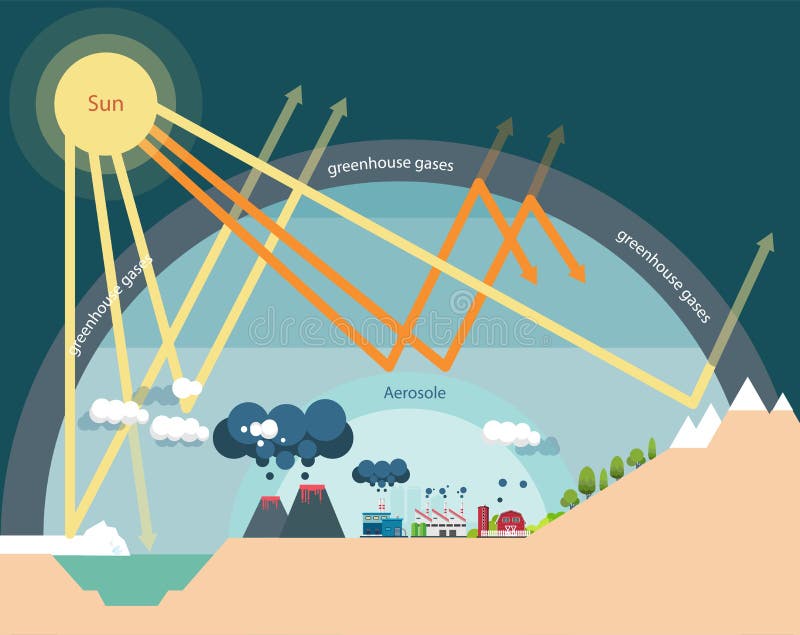



Effect Greenhouse Stock Illustrations 3 3 Effect Greenhouse Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



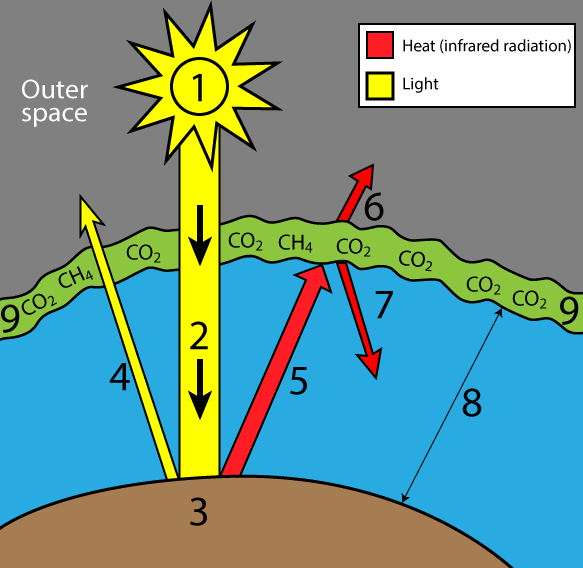
5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube
The Greenhouse Effect If it were not for greenhouse gases trapping heat in the atmosphere, the Earth would be a very cold place Greenhouse gases keep the Earth warm through a process called the greenhouse effect Play the video to learn more » Greenhouse Gas Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 2530% Futtsu Thermal Power Station near Tokyo Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels like coal, natural gas and oil produces more greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions than any human activity, accounting for at least one quarter of all global emissions Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time




Understanding The Greenhouse Effect Learn Biology




Greenhouse Effect Carbon Dioxide Methane Teaching Resources
Important Greenhouse Gases (concentrations in parts per million volume) water vapor 0140,000 carbon dioxide 370 methane 17 nitrous oxide 03 ozone 001 chlorofluorocarbons ~ A greenhouse gas is defined as a gas that absorbs significantly the radiation emitted by the Earth and its atmosphere (Infrared, IR, or longwave radiation)The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon in which the specific gases in the atmosphere of the Earth trap heat from the sun (see The Greenhouse Effect Diagram attachment) Typically, our atmosphere absorbs just the right amount of heat so that living things can surviveAnd ozone, which causes 3–7 percentThe issue is how the strength of the greenhouse effect changes when human
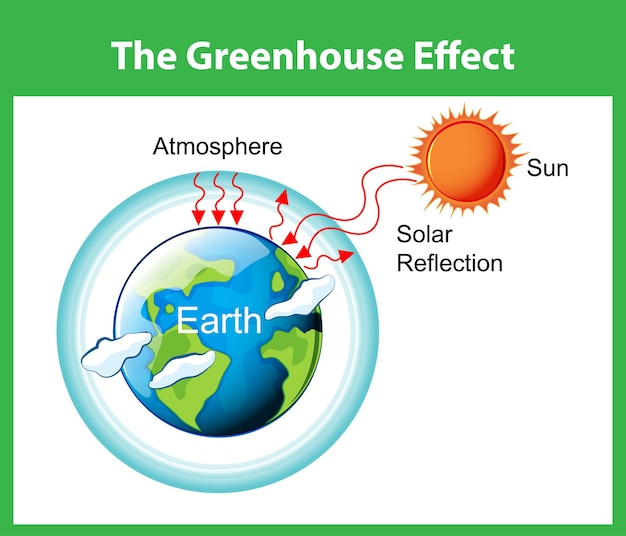



Free Vector The Greenhouse Effect Diagram




12 445 Greenhouse Effect Stock Photos And Images 123rf
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)On Earth, the major greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 36–70 percent of the greenhouse effect (not including clouds); The gases present in the atmosphere for example ozone, methane, carbon dioxide, water vapour and chlorofluorocarbons are called greenhouse gases, they absorb some heat thereby restricting the heat to escape our atmosphere These gases add to the heating of the atmosphere and result in global warming In places where the temperature is low, we



File Greenhouse Effect Svg Wikimedia Commons




Small Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram Full Size Png Download Seekpng
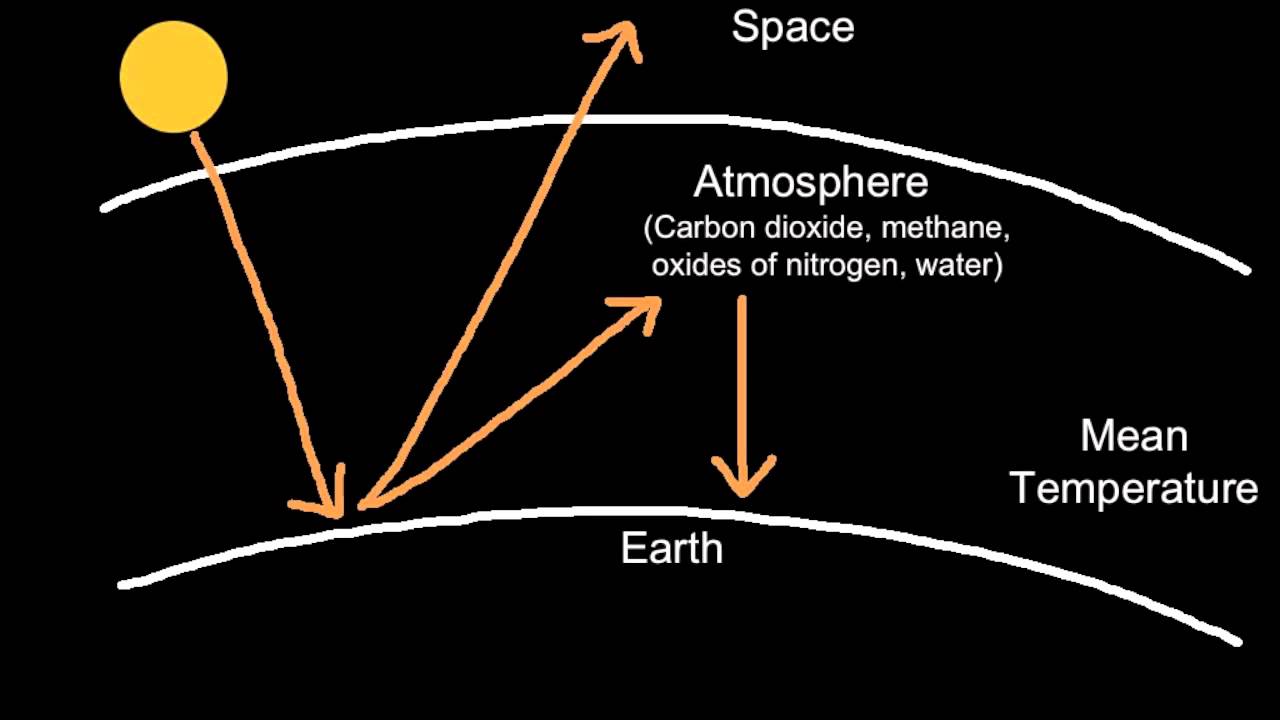
However, greenhouse gases will not let all the infrared light pass through the atmosphere1 They absorb some and radiate it back down to the Earth This phenomenon, called the greenhouse effect, is naturally occurring and keeps the Earth's surface warm It is vital to our survival on Earth Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's averageThe greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would beIn order to properly understand the greenhouse effect one must take into account the nonlinearity of the effect of increased concentration of greenhouse gases One must also take into account that different greenhouse gases may have different spectra for the absorption of thermal radiation In the diagram below the increase from A to B




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences



Greenhouse Gasses Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail U S National Park Service
To the right is a diagram (also from NOAA, ESRL, the same source as the table above) which illustrates the greenhouse effect Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (round about the late 1700's), the concentration of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere has rocketed by an estimate of 30%, most significantly carbon dioxideActivity 12 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 5 – 6 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will complete a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinion questions, and perform a skitThe greenhouse effect plays a significant role in Earth's energy budgetWith the natural greenhouse effect, the energy budget is balanced as thermal radiation is reradiated towards the ground, trapping thermal energy and warming the Earth However, with the greenhouse effect being enhanced by humans, the energy budget of the Earth is shifted to an imbalance




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlightMethane (CH 4), which causes 4–9 percent;Methane, which causes 49%, and ozone, which causes 37% It is not possible to state that a certain gas causes a certain percentage of the greenhouse effect, because




File Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Wikimedia Commons




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Greenhouse gases (mainly carbon dioxide and methane) above the natural amount, which has led to increased warming Figure 3 Diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect TheEnergy resources diagram "Consumption of energy resources, (eg turning on a light) requires resources and has an effect on the environment Many electric power plants burn coal, oil or natural gas in order to generate electricity for energy needs While burning these fossil fuels produces a readily available and instantaneous supply of




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
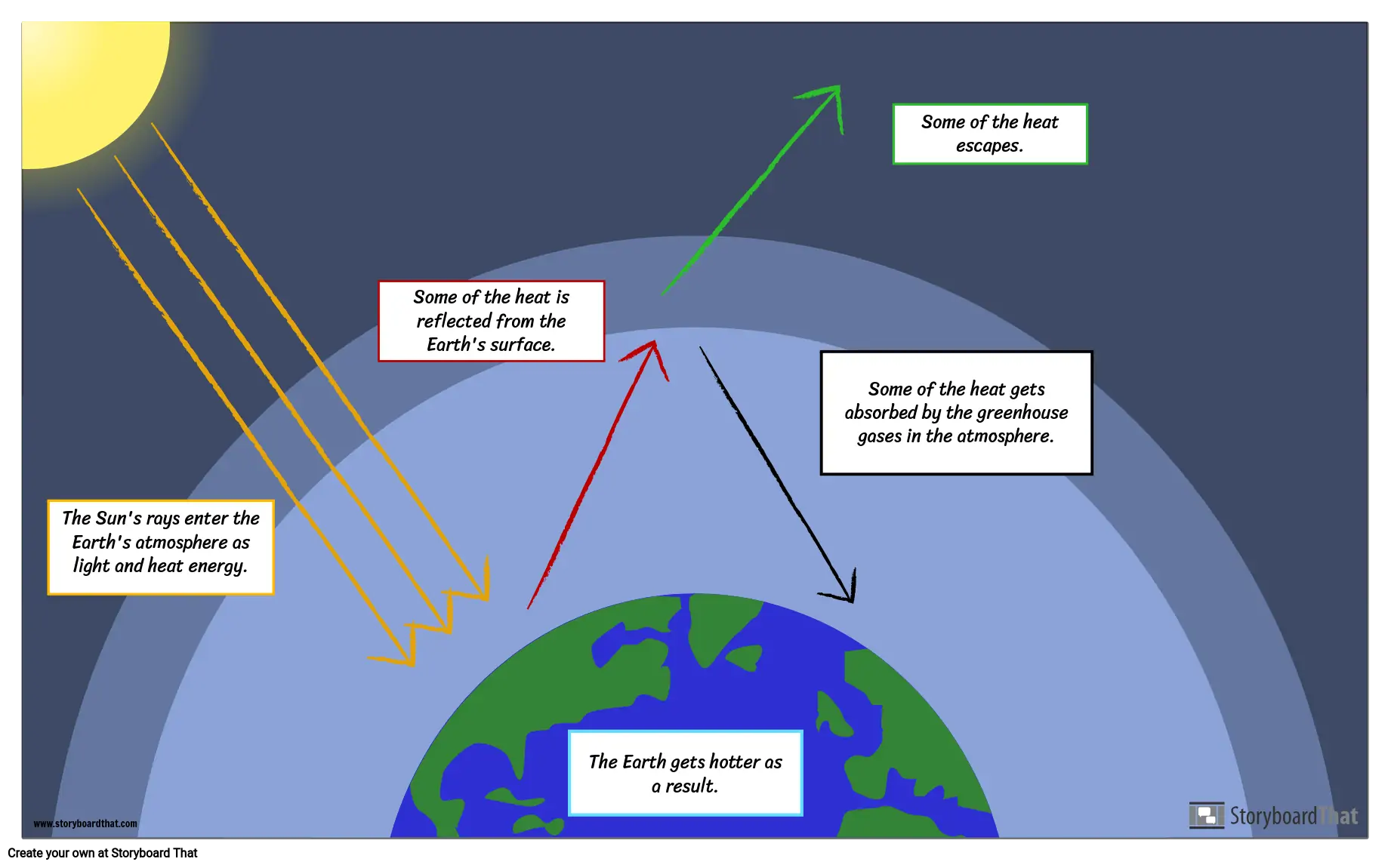



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Greenhouse Gases Quotes Quotesgram




Representation Of The Natural Greenhouse Gas Effect Higher Levels Of Download Scientific Diagram




Illustration Of The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Free Vector The Greenhouse Effect Diagram



Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Uae Teacher



Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustration Illustration Of Global




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect World101
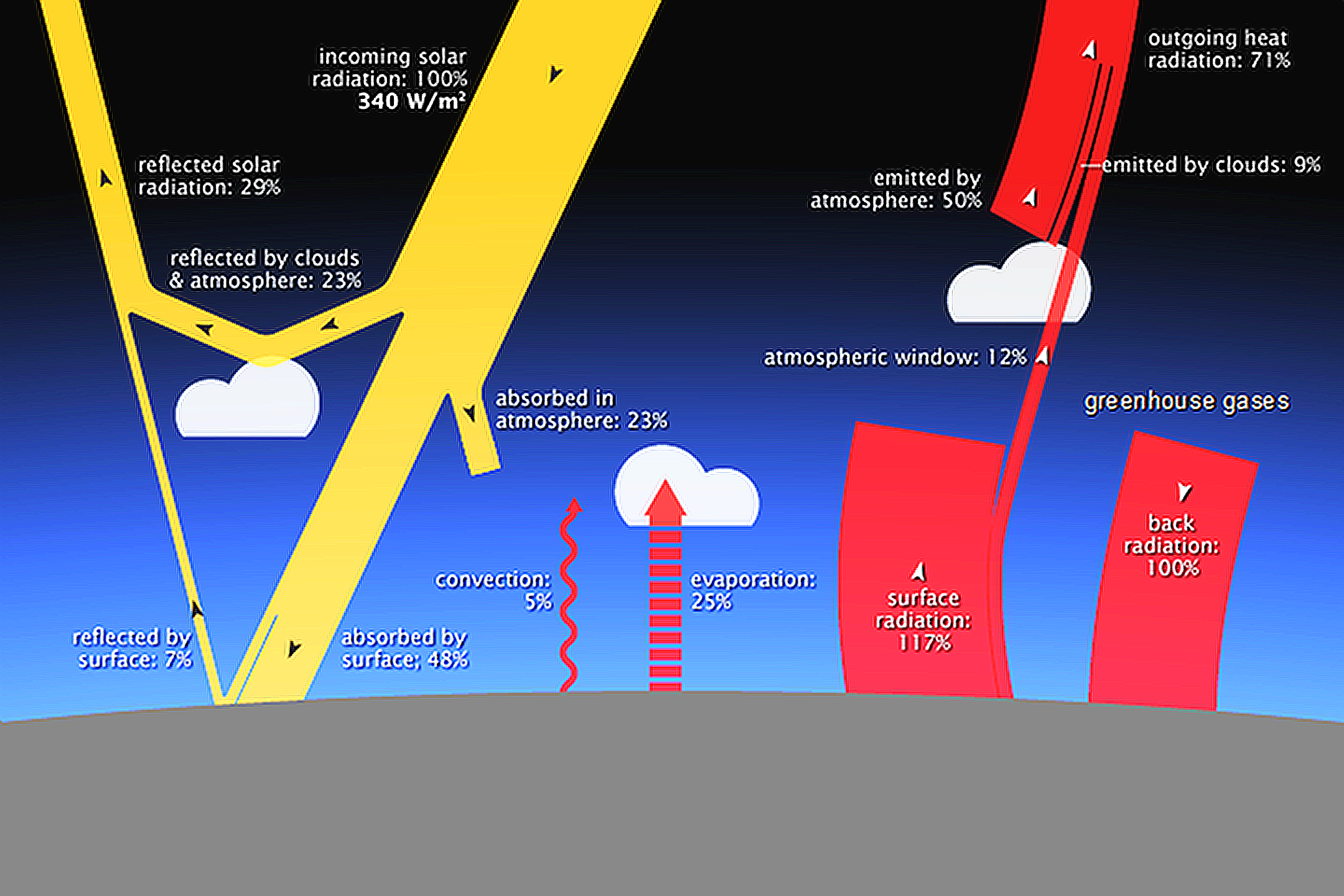



Schools For Future




Canada Needs To Increase Efforts To Cut Down Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ptc Punjabi Canada Canada News Punjabi News Canada Brampton News




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering
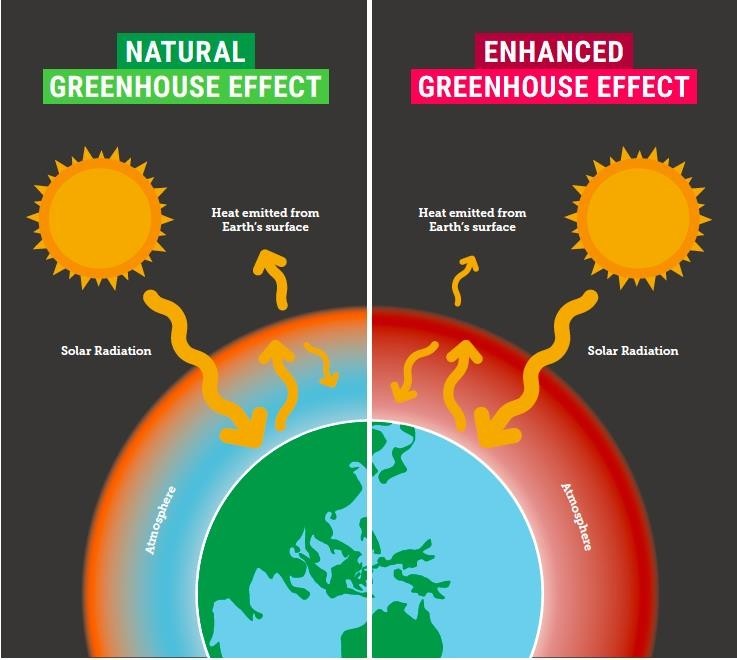



The Greenhouse Effect Sustainable Energy Network Solutions




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




What Is Natural Greenhouse Effect Facts And Climate Change Average Temperature Of Planets And Earths Temperature Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Schematic Of Greenhouse Gas Effect 8 Download Scientific Diagram
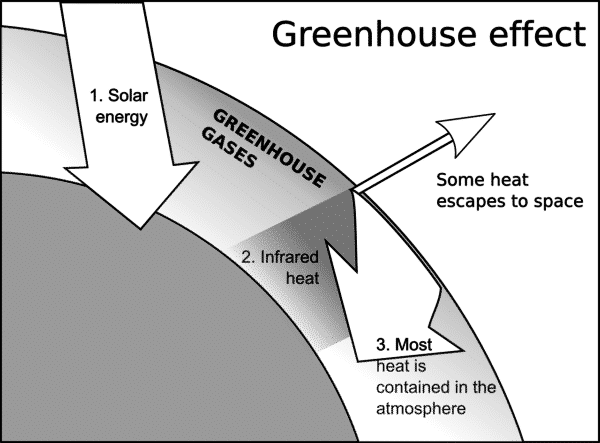



What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub



3



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




The Albedo Effect Or Greenhouse Effect Source Sankey Diagram Efectos Del Calentamiento Global Gases Invernadero Cambio Climatico




Carbon Flux Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet
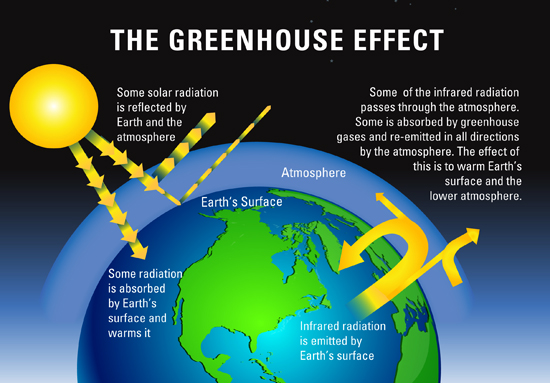



Diagram That Explains Greenhouse Effects Climate Change
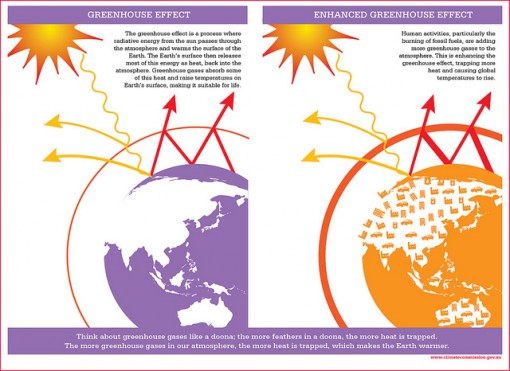



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Igcse Biology 17 4 15 Understand How An Increase In Greenhouse Gases Results In An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect And That This May Lead To Global Warming And Its Consequences
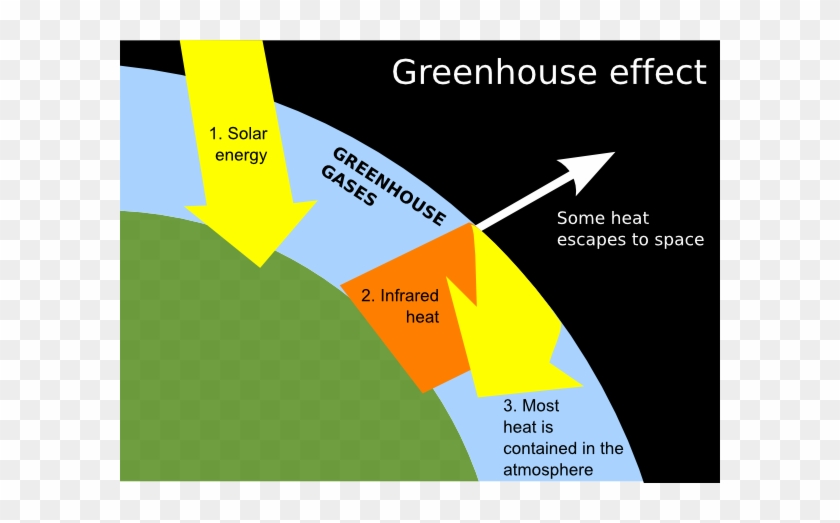



Greenhouse Clip Art At Clker Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download
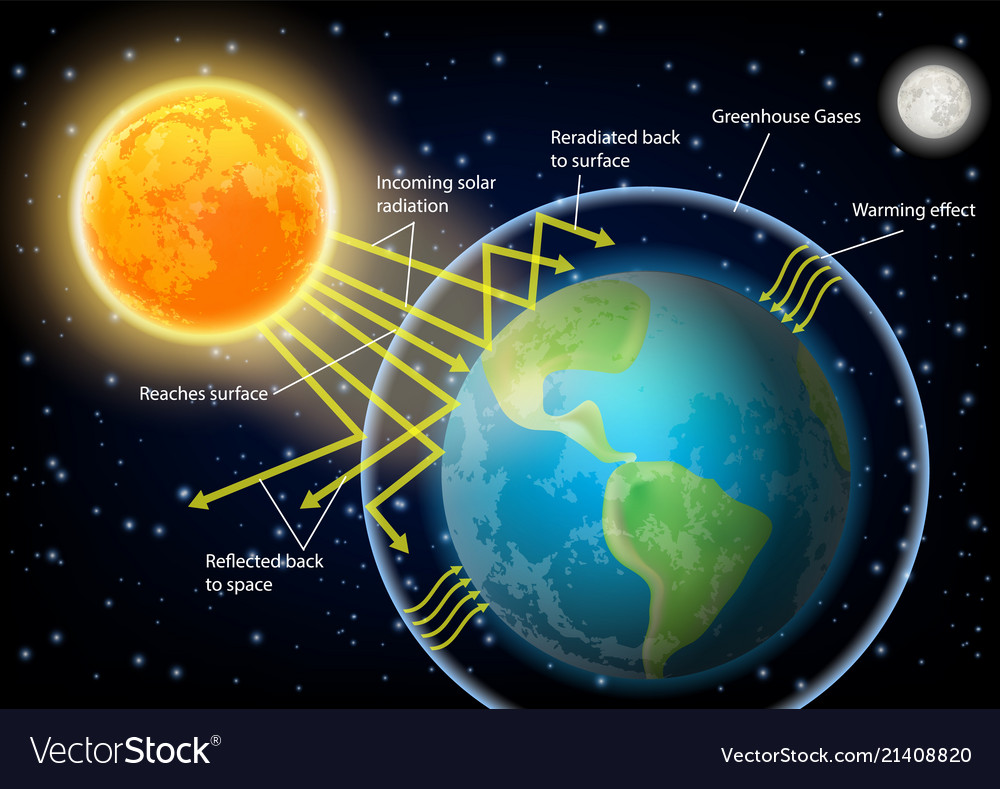



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image



Greenhouse Gases




Decomposition Of Metal Carbonates And Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet
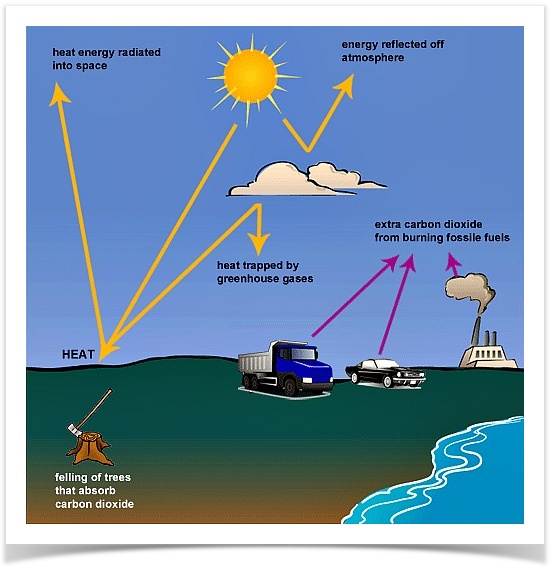



Graph Writing 162 Greenhouse Gases Trap Energy From The Sun
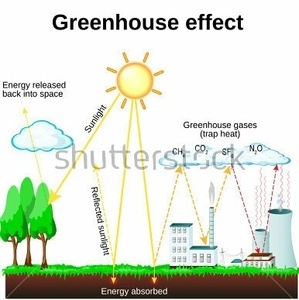



Greenhouse Effect Mind Map




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
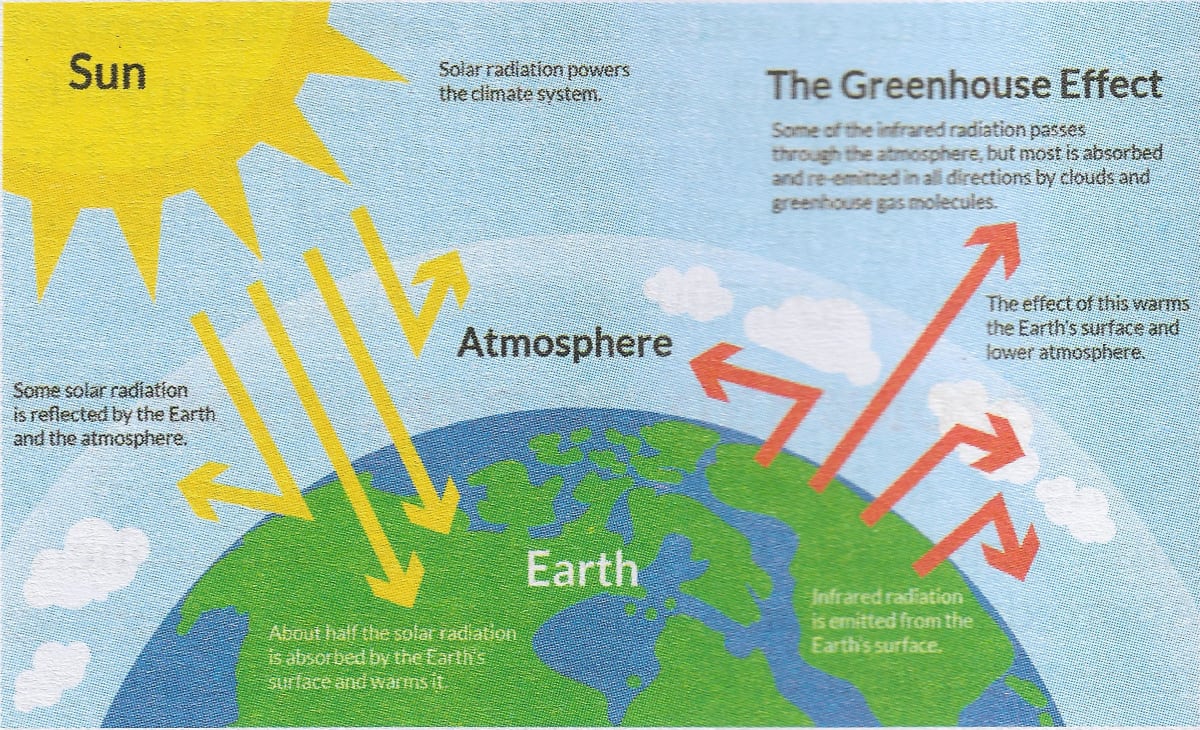



Draw A Well Labelled Diagram To Explain The Greenhouse Knowledgeboat




Climate Change Basics Ag Matters




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases
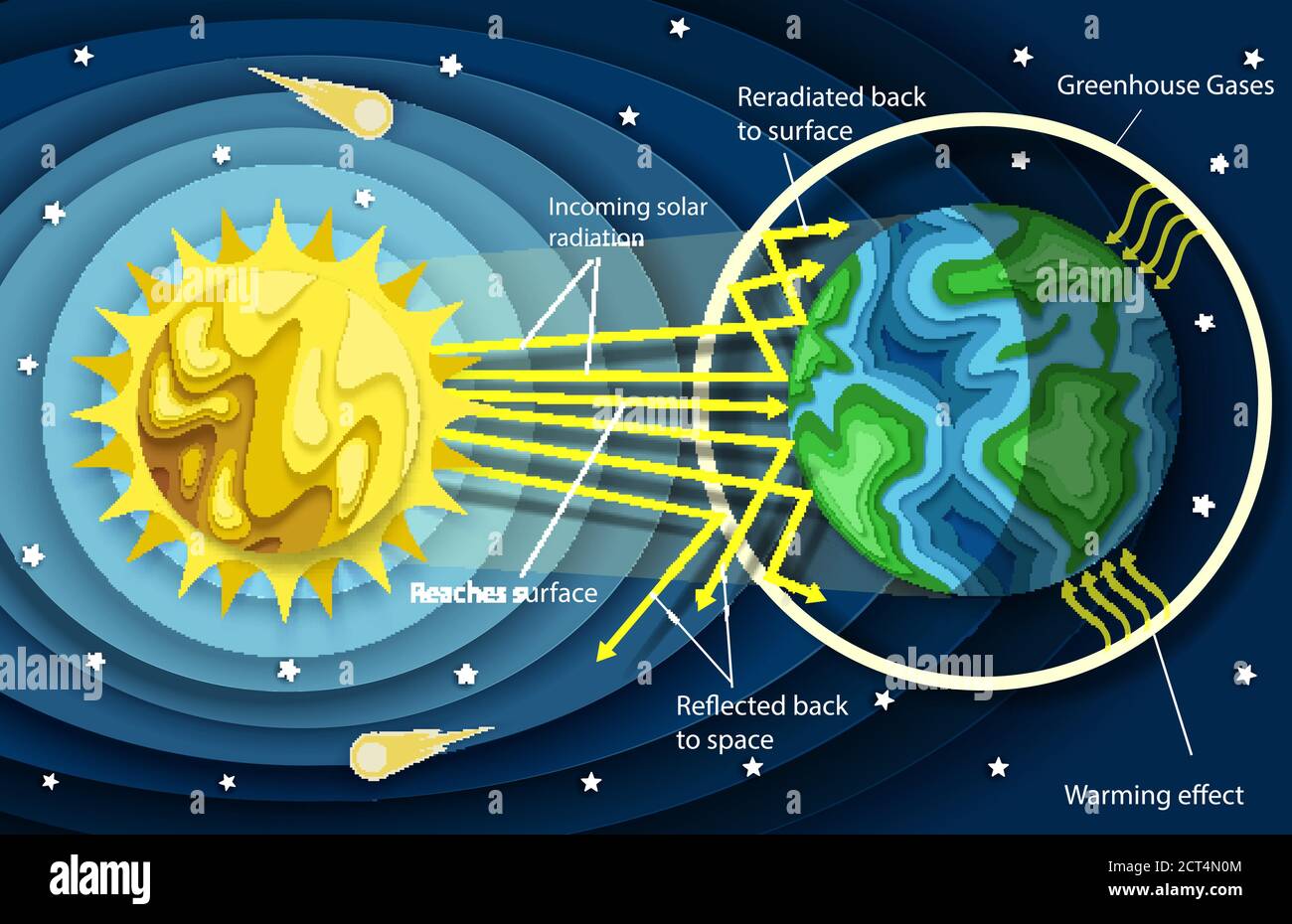



The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Vector Image Art Alamy




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com
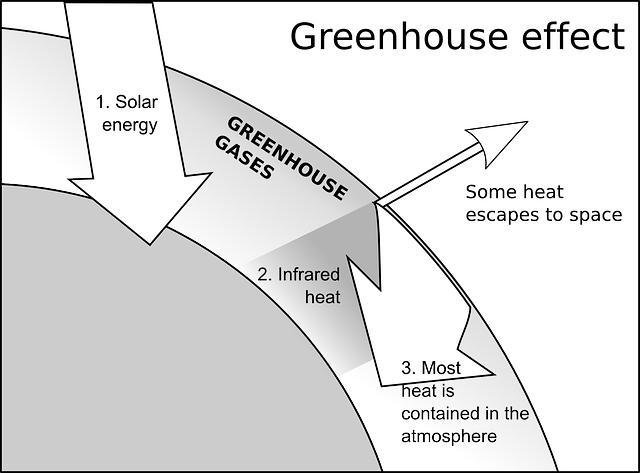



What Is Greenhouse Effect And What Are Greenhouse Gases Earth Eclipse
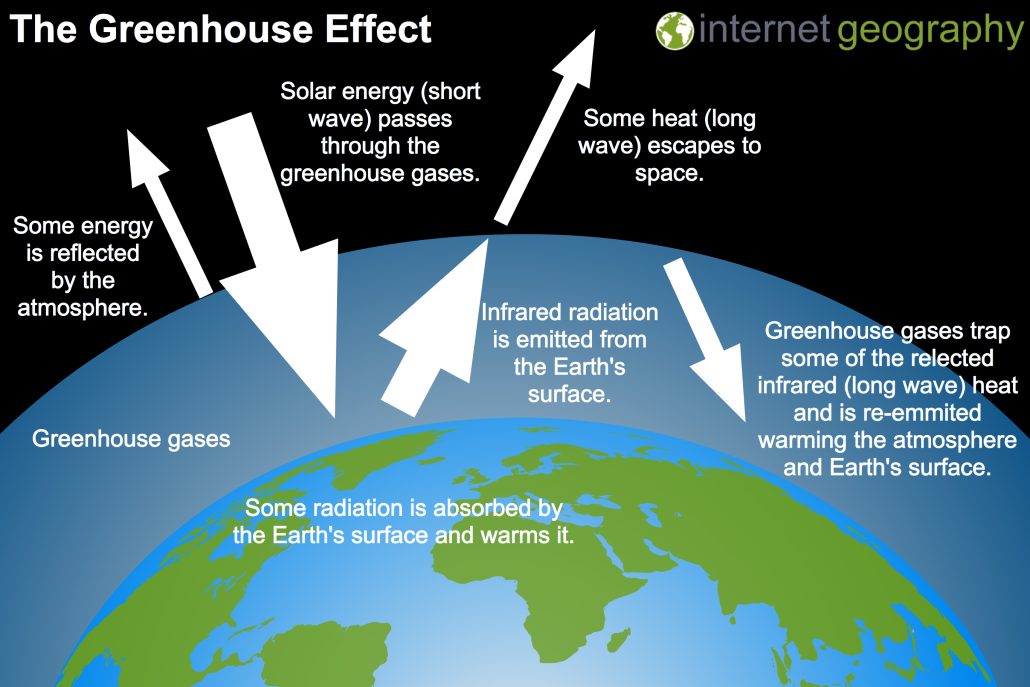



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography
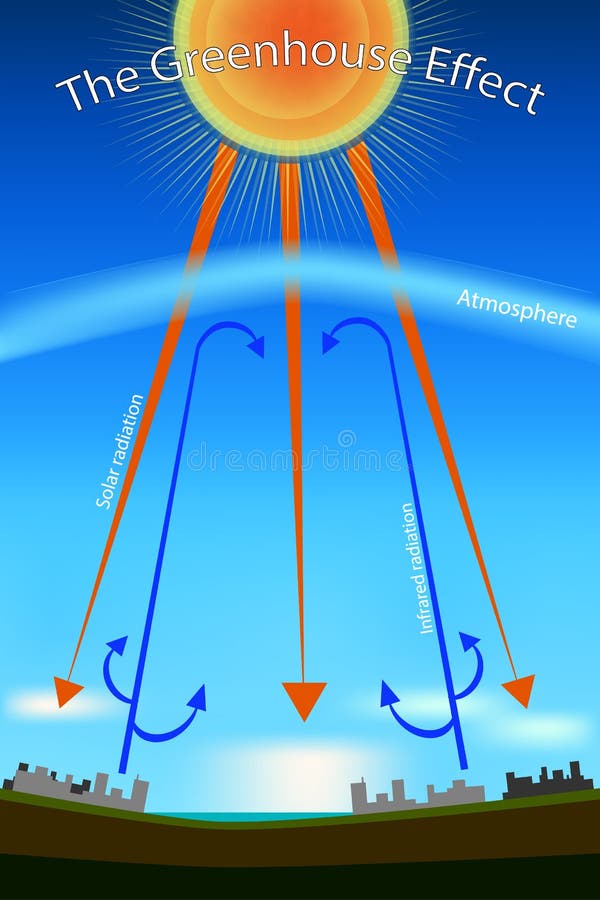



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 165 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect



1




Diagram Of The Greenhouse Gas Effect Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




Warm On Top Cold Below Unexpected Greenhouse Gas Effect In Lakes




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated
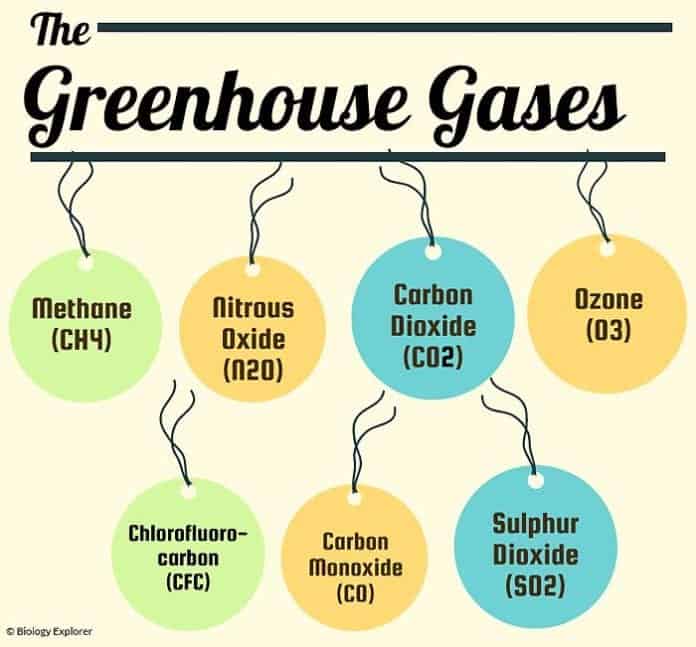



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Design Emission




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change




Greenhouse Effect Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation




Free Vector The Greenhouse Effect Diagram
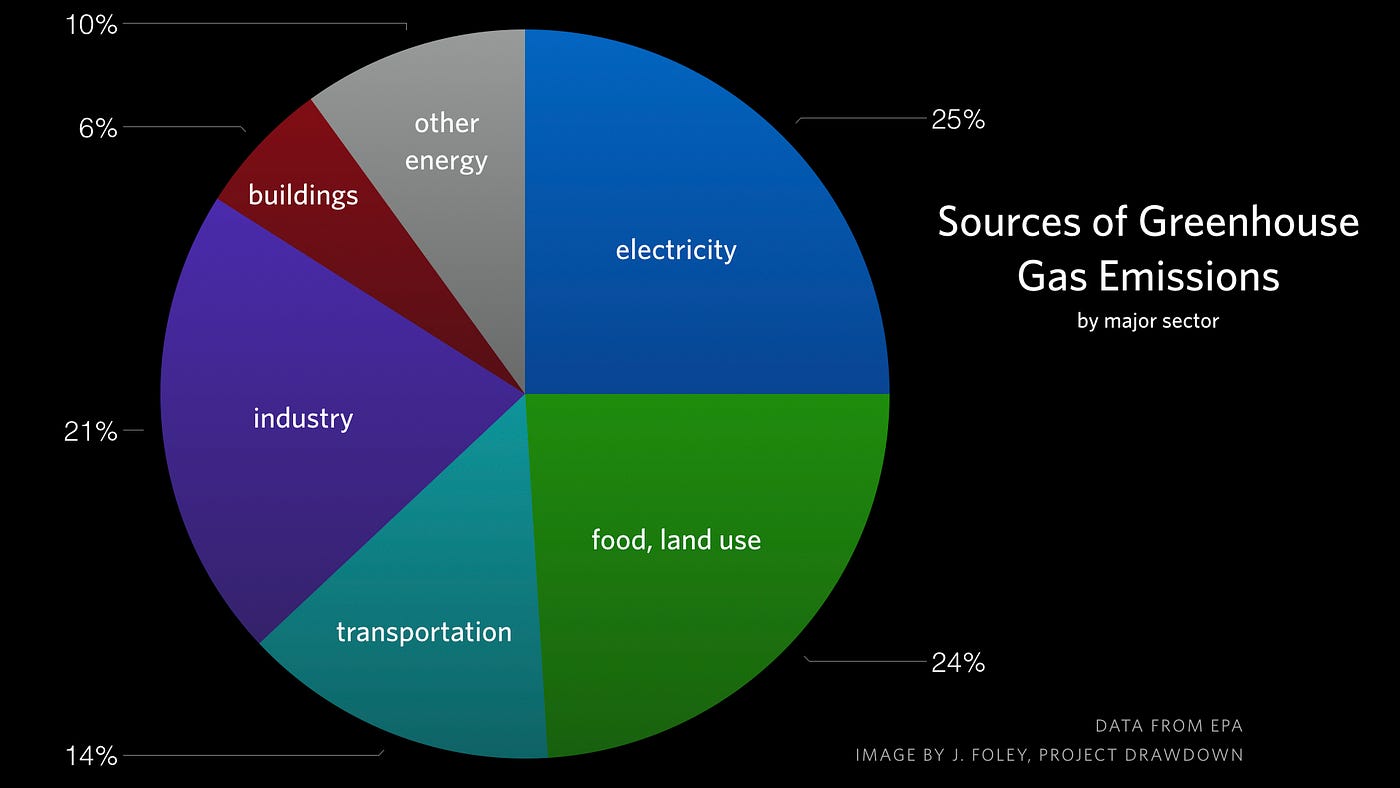



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org



Simple



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change
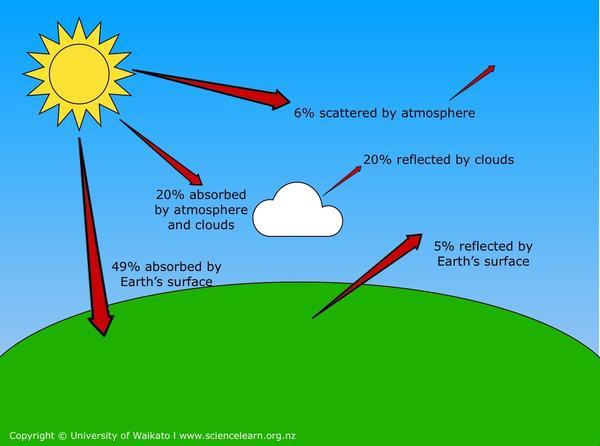



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub
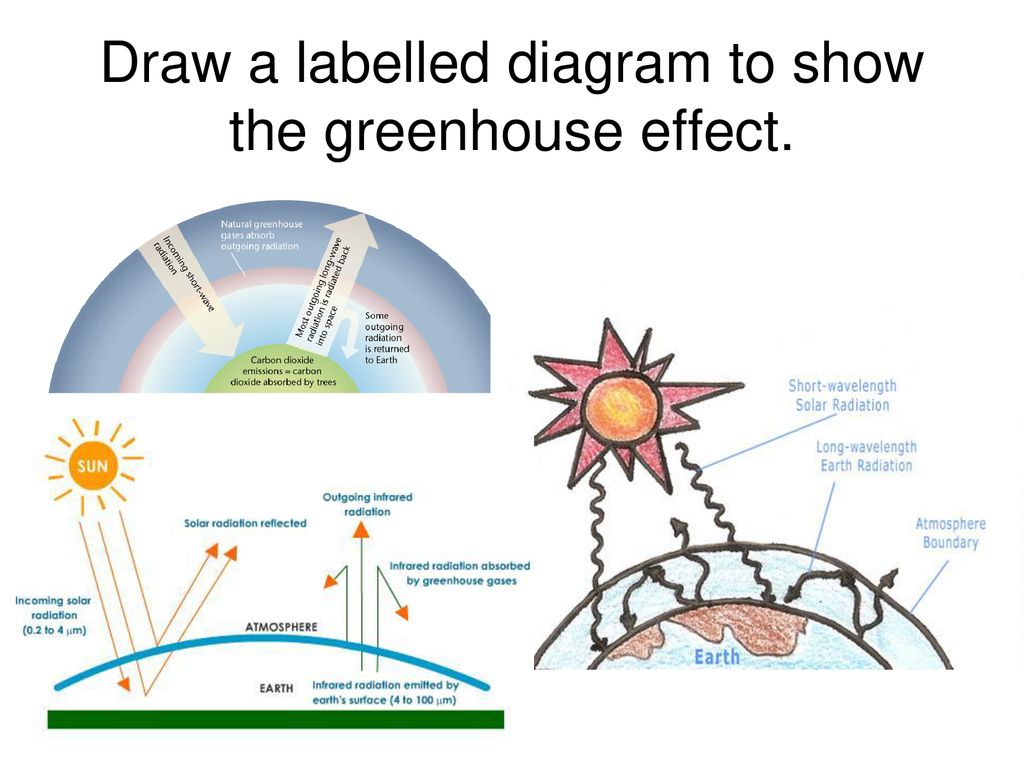



Lesson Ppt Download




Greenhouse Gases Quotes Quotesgram
コメント
コメントを投稿